Mission
Our goal is to understand how resistance to therapy develops in children with cancer, and how it can be prevented.
Research Activities
|
Epigenetic mechanisms of drug resistance
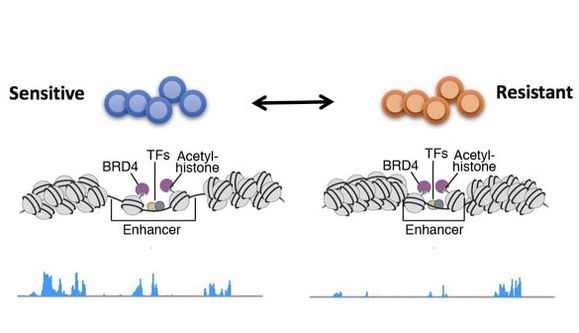
Many types of cancer are characterized by a great degree of heterogeneity, both on a genetic and a functional level, and the ability to adapt to therapeutic agents in a reversible manner. For example, we have shown that inhibition of the NOTCH1 pathway leads to development of drug resistance in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) via epigenetic regulation of the BET family member BRD4. Inhibition of BRD4 with small molecules represents an approach to overcome this resistance. Investigating the epigenetic regulation that leads to the adaptive changes of resistance may reveal novel targetable molecules and pathways. |
|
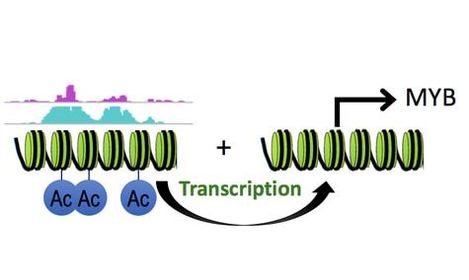
Transcriptional rewiring in cancer
Transcriptional networks play a crucial role for promoting growth of pediatric malignancies, but their regulation is complex. Understanding the interplay between enhancers, promoters, transcription factors and other elements of the transcriptional machinery is crucial for understanding the oncogenesis of pediatric malignancies as well as for understanding the basis of drug resistance. We are developing novel next-generation sequencing approaches to decipher this interplay. We deploy computational strategies to 3-dimensionally characterize the changes in the gene-regulatory machinery as malignant cells become resistant to therapy. |
|
Targeting the transcriptional machinery of pediatric malignancies and the immune system
Strong activity of oncogenic transcription complexes are a hallmark of many types of cancer in children. However, transcription factors are notoriously difficult to target therapeutically. Targeting enzymes that propagate modification of histones, DNA and transcription complexes represent an indirect way to exploit vulnerabilities of the transcriptional machinery. Changes in this machinery occur in the cancer cells themselves as well as in the associated immune microenvironment. We are exploring approaches to manipulate these processes. |